Lingocode
A downloadable tool for Windows
#
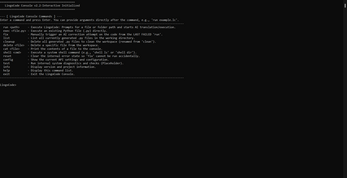
🚀 LingoCode Interactive Console (v4)
‼️NEW : add a way to run local modules download them and run them only by usuing Lingocode nothing else needed.
‼️and install manger
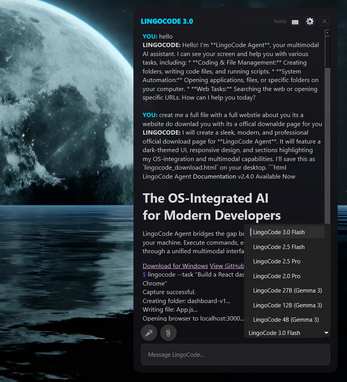
Welcome to LingoCode, your personal AI-powered developer console! This tool allows you to write plain English instructions (in a file or directly in the console) and have the system translate them into complete, runnable code in any programming language.
It's designed to be a "self-healing" environment, meaning if the generated Python code fails, the console will automatically try to fix it.
## 📋 Table of Contents
- [Overview: How it Works Internally](#-overview-how-it-works-internally)
- [Running the Console](#-running-the-console)
- [Special Features](#-special-features)
- [Command Reference](#-command-reference)
- [Example Workflows](#-example-workflows)
## 💡 Overview: How it Works Internally
The LingoCode executable contains a full command-line interface that manages a powerful AI code engine. It handles everything internally to provide a seamless experience:
1. **Instruction Input:** You give the system an instruction using the `run` command (e.g., "make a hello world script").
2. **AI Translation:** The console sends your prompt to the private code engine, which translates your natural language idea into structured code files (e.g., Python, HTML, C++).
3. **File Management:** The console automatically saves all the files the AI generated into your local folder.
4. **Execution and Self-Healing:** If Python files are created, the console runs them. If a runtime error occurs, the console instantly captures the failure, sends the error trace and the bad code back to the AI, and requests a correction. It can try to fix the code up to 3 times automatically.
### More information
**Download**
Lingocode3.exe (81 MB)
**Install instructions**
Standalone executable. No installation required.
## 💻 Running the Console
Since LingoCode is a standalone application, starting it is simple!
REPL stands for "Read-Eval-Print-Loop." It means the application runs in a continuous loop, constantly waiting for your command.
To start the console, just run the compiled executable file (named `lingocode_cli.exe`)
| Updated | 13 days ago |
| Status | In development |
| Category | Tool |
| Platforms | Windows |
| Author | Deathrazor |
| Tags | artificial-intelligence |
Download
Install instructions
OLD Version below new version only extacte what inside the ZIP:
💻 Running the Console
Since LingoCode is a standalone application, starting it is simple!
REPL stands for "Read-Eval-Print-Loop." It means the application runs in a continuous loop, constantly waiting for your command.
To start the console, just run the compiled executable file (it is likely named lingocode_cli.exe or similar) from your terminal:
./lingocode_cli
You will see the welcome message and a colored prompt that looks like this:
LingoCode>
Now you can type any of the commands listed below!
✨ Special Features
- REPL Mode (Direct Prompting): You don't need a separate instruction file! You can type your idea directly after the
runcommand.LingoCode> run "make a red button in an html file"
- Multi-Command Execution: You can run several commands at once by separating them with a semicolon (
;).LingoCode> run "make hello.py" ; exec hello.py ; cleanup
- Prompt Color Change: Use the
colorcommand to personalize your console prompt.LingoCode> color blue
📚 Command Reference
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| run <path/prompt> | The primary command. Translates your idea into code. You can provide a path to a .lc file, a folder, or a direct text prompt.
|
| exec <file.py> | Executes an existing Python file and shows the output. |
| fix | If a previous run command failed, this manually triggers another AI correction attempt using the last recorded error.
|
| build <file.py> | Packages a Python script into a single, standalone executable (like an .exe). Places the file in a new dist folder.
|
| list | Shows a list of all files the AI has generated in your current folder (e.g., .py, .html, .js, .cpp).
|
| cleanup | Deletes all generated files in the folder to give you a clean workspace. It requires confirmation first. |
| delete <file> | Deletes one specific file (e.g., delete main.py).
|
| cat <file> | Prints the entire contents of a file directly into the console for you to read. (Short for "concatenate"). |
| shell <cmd> | Lets you run a system command, like shell ls (on Mac/Linux) or shell dir (on Windows) to check your files.
|
| color <name> | Changes the color of the LingoCode> prompt. Type color help to see all available color options.
|
| reset | Clears the console's memory of the last error. This disables the fix command until a new error occurs.
|
| config | Shows the current script version and configuration details. |
| info | Displays the version and a brief description of the LingoCode project. |
| help | Prints the full list of all available commands (like this table!). |
| exit | Quits the LingoCode console. |
💡 Example Workflows
Example 1: Basic Python Script
LingoCode> run "make a python file called hello.py that prints 'Hello from the AI'"LingoCode> exec hello.pyLingoCode> listLingoCode> cleanup
Example 2: Multi-Command Workflow
This one-liner does the work of four separate commands!
LingoCode> run "make a simple calculator in python" ; exec main.py ; list ; cleanup
Example 3: Building an App
LingoCode> run "make a tkinter app with a single button that closes the app"LingoCode> exec main.py(A window should pop up!)LingoCode> build main.pyLingoCode> shell dir(Look for the 'dist' folder where the executable is saved)